Optimizing Project Planning and Material transportation
This article was originally published on November 26, 2023 on linkedin.com

Pieter Bruegel the Elder. "Hunters in the Snow"
Today I’m going to continue the exploration of optimization problems. So, this article delves into two distinct types of problems that can be efficiently tackled through Python programming: optimal transportation and resource allocation.
While the transportation problem can be solved using other solvers (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_optimization_software), I found that CPLEX is the most suitable choice for scheduling problems, particularly in industries like construction where project planning software like Primavera and MS Project is commonly used. CPLEX distinguishes itself from other solvers by offering constraints for the delay and task sequence modelling, as described in the IBM documentation (https://www.ibm.com/docs/en/icos/22.1.1?topic=manual-functions). These constraints allow for more accurate modelling of real-world scheduling scenarios, making CPLEX a valuable tool for optimizing project schedules.
Part 1. The way of transportation
Picture this: you’ve got five construction sites and three sand quarries. And there is the task of figuring out the optimal way to distribute sand without burning too much fuel (measured in tonne-kilometres). The details are all laid out in a table:
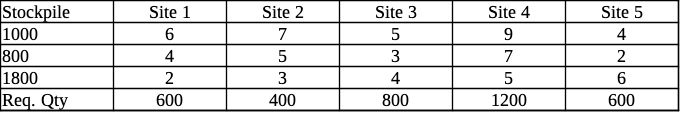
In the tutorial you can find the similar task:
The supply capacity is indicated with the supply nodes, while the demand is indicated with the demand nodes, and the transportation costs are indicated on the arcs.
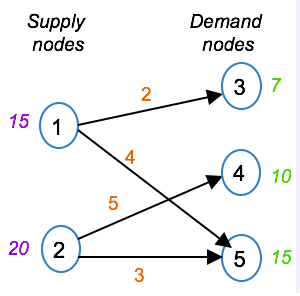
The Transportation Problem example
I’m not dropping the code here, but if you want to check it, click the link below.
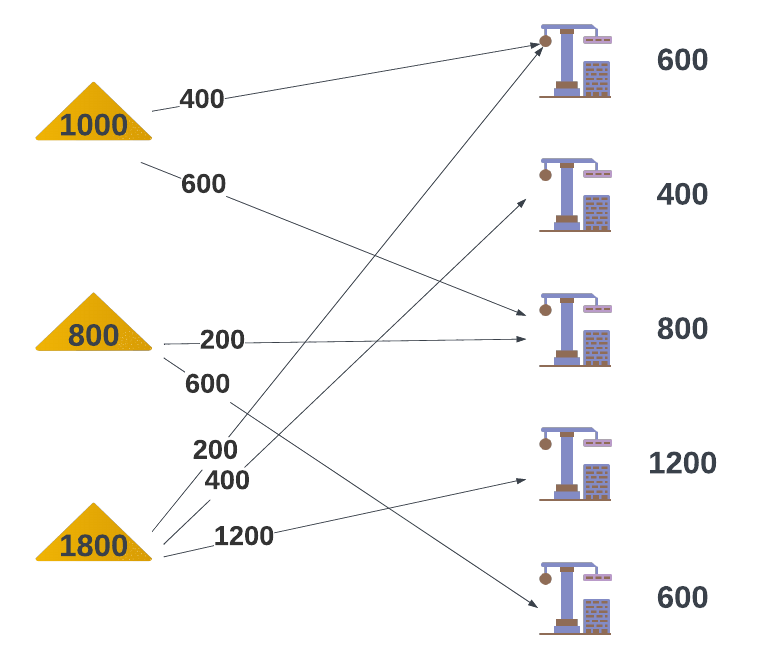
Here we have our solution:
Part 2: Optimal Resource Allocation
When it comes to our scheduling endeavours, we’d prefer terming it as optimal resource allocation. Undoubtedly, the pivotal aspect of project planning revolves around allocating resources in a manner that ensures a seamless and balanced distribution.
Planning software, such as Primavera, can automatically resolve schedules using the critical path method or resource levelling. In the first option, it calculates the optimal project duration without considering the availability of resources. On the other hand, the second option, resource levelling, while taking resource availability into account, does not consider task deadlines for the optimal total project duration. It resolves conflicts by adjusting task dates, allowing tasks to be delayed without considering the project deadline.
All of this is not to mention the consideration of financial schedules.
To effectively address these conflicts, the most flexible approach is schedule optimization using LP solvers. Below, I’ll illustrate this with an example.
As an illustration, consider Chapter 5 in the CPLEX Tutorial, addressing the following problem:
There are three workers, and each task requires any one of the three workers. A worker can be assigned to at most one task at a time. In addition, there is a cash budget with a starting balance. Each task consumes a certain amount of the budget at the start of the task, and the cash balance is increased every 60 days.
CPLEX can solve it in this way, getting a total project duration of 285 days:
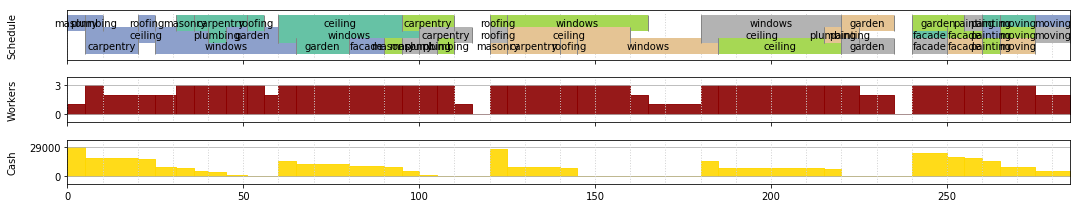
Profile in the Jupyter Notebook
To clarify the impact of optimization, let’s remove the budget and calculate the schedule in Primavera. Now, let’s see what results we obtain.
Let’s start with calculation with CPLEX.
Check out the full Jupyter Notebook here
After optimization, we achieved a project duration of 265 days and a smoothed profile without overallocation (XER file).
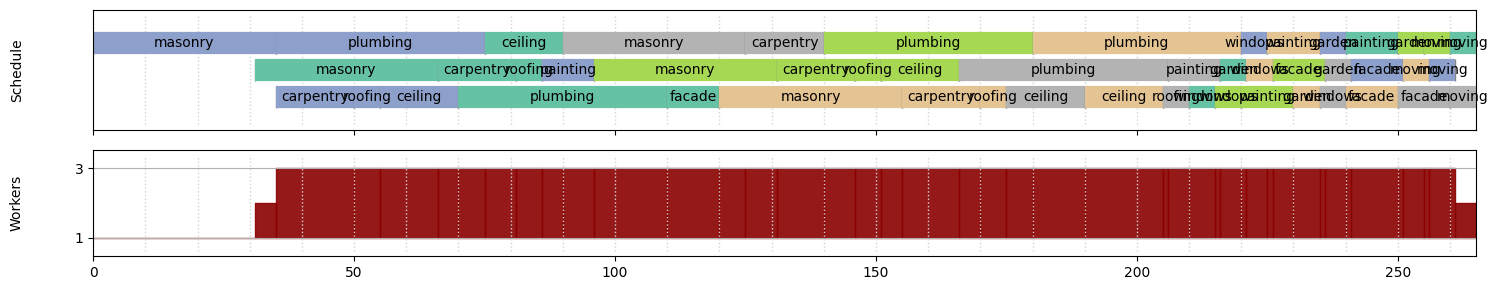
Profile in the Jupyter Notebook
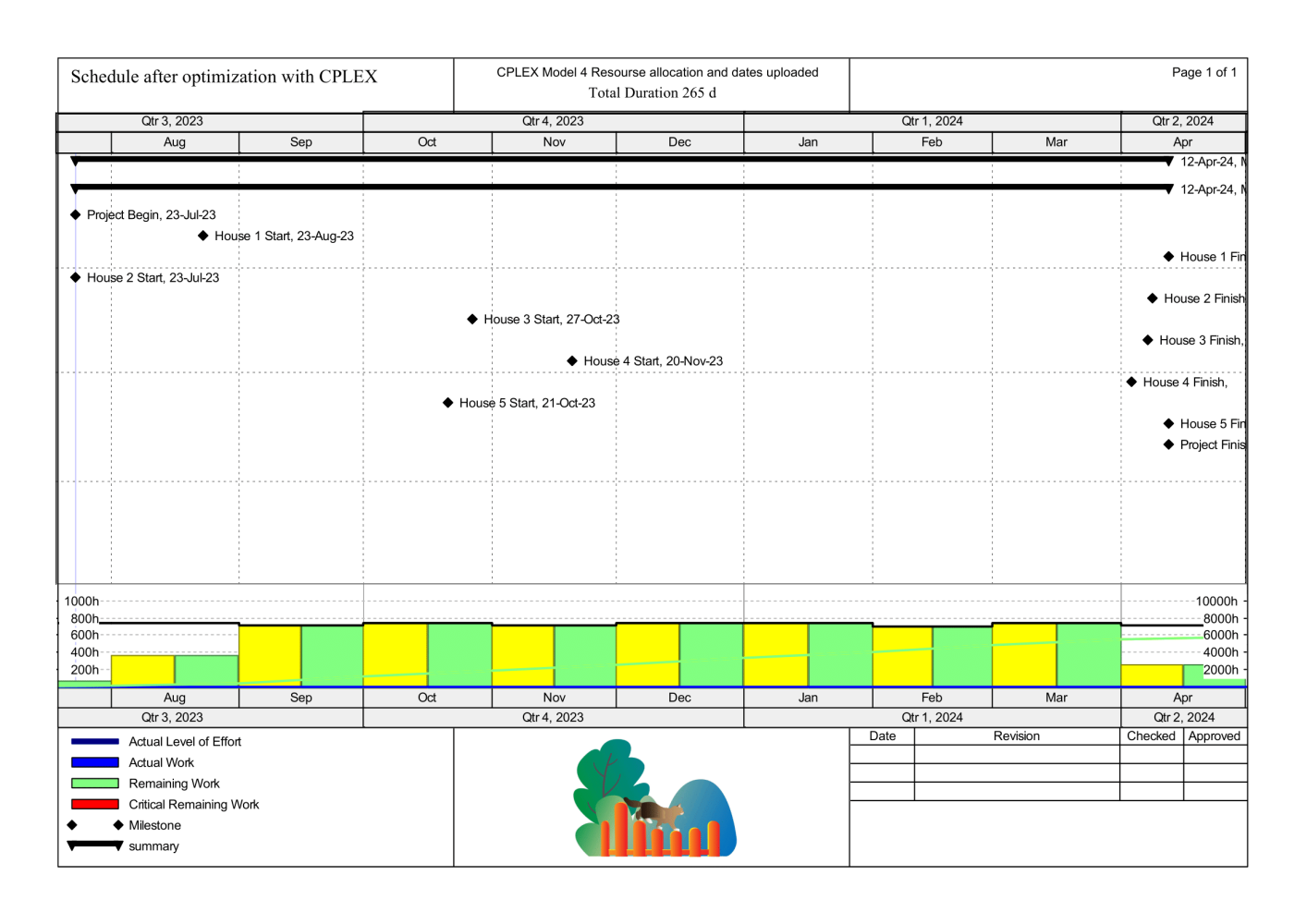
Gantt chart and resource profile for LP optimized schedule
While, without prior optimization with a simple calculation of the dates, we get a schedule for a project duration of 210 days (XER file), but featuring resource overallocation:
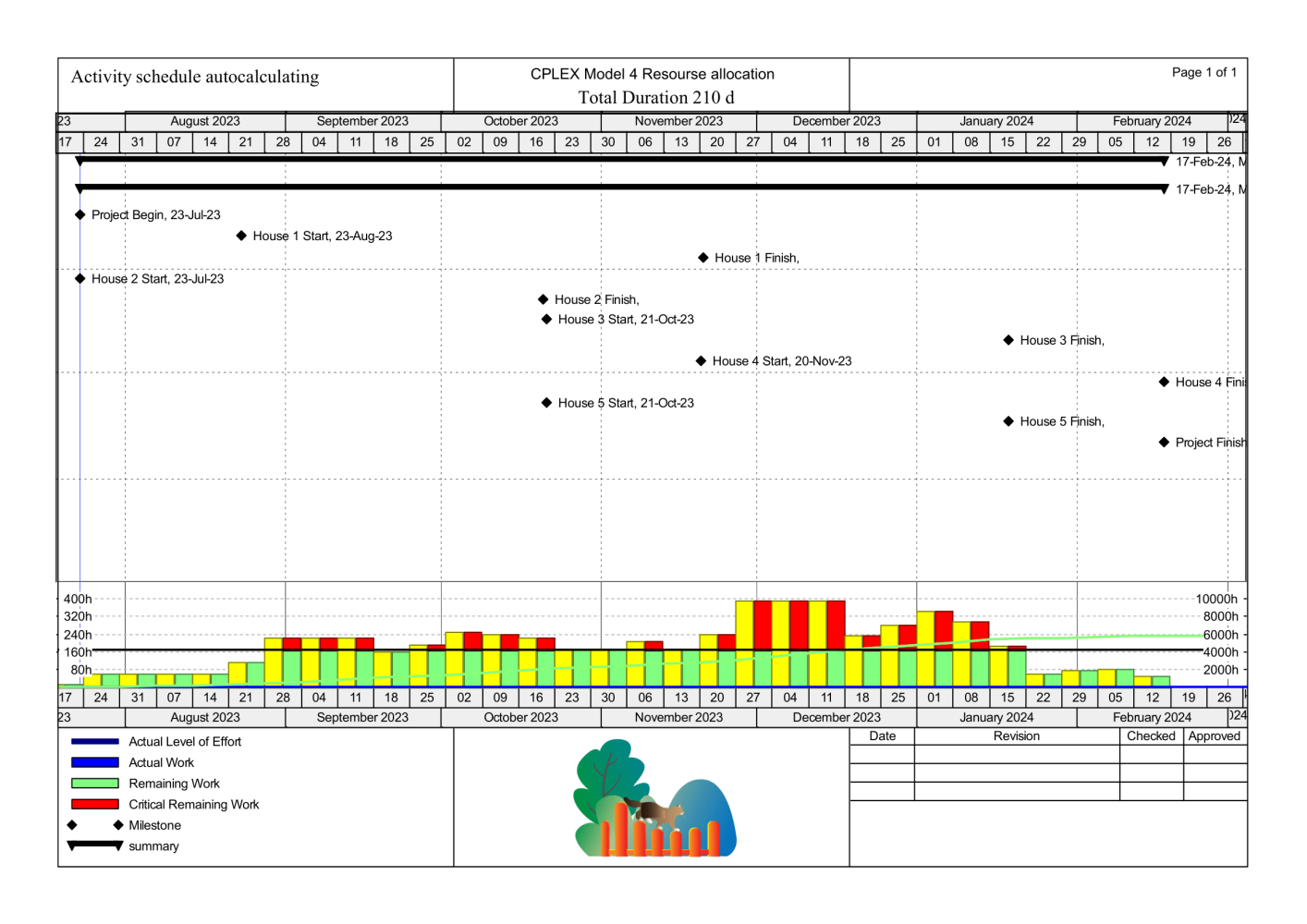
Gantt chart and resource profile after schedule P6 calculation
And 376 days (XER file) of project duration with resource auto levelling:
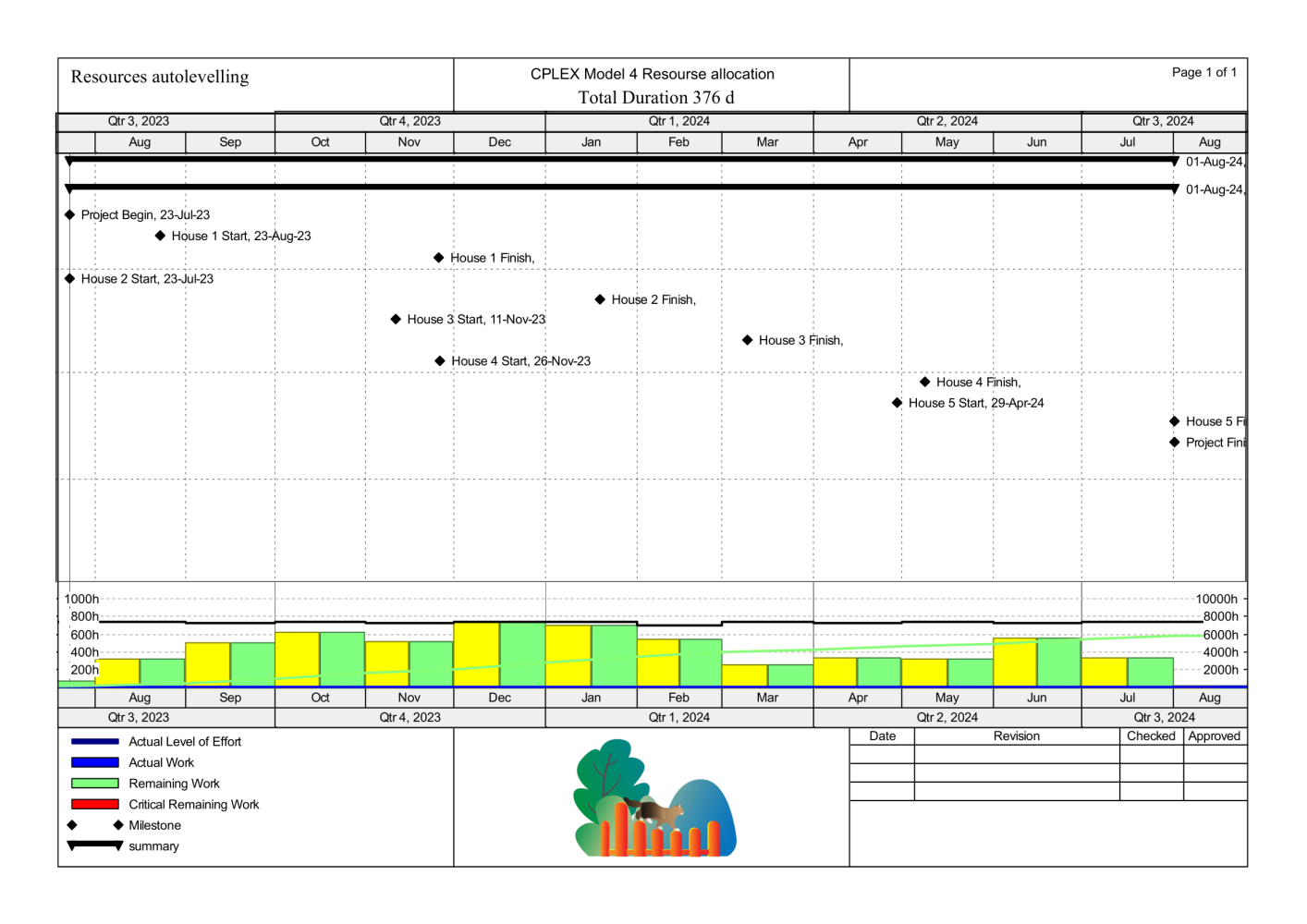
Gantt chart and resource profile after schedule P6 resource auto levelling
Certainly, we can manually address overallocation by adjusting activity dates and reaching an optimal solution through compromise. Yet, the question remains: will this truly be the best solution?
As a bonus, I’d like to highlight an important advantage of using optimization tools like CPLEX: the XER file parsers, such as PyP6Xer or xerparser. This provides the opportunity to read XER files for optimization. However, we’ll delve into these features in the next episodes.
In conclusion, this journey into optimization techniques using Python, particularly with CPLEX, emphasizes the importance of leveraging LP solvers to tackle intricate scheduling challenges. The showcased solutions demonstrate how optimization tools wield the power to streamline resource allocation, resulting in enhanced project timelines and more effective resource management.
#ProjectScheduling #ResourceAllocation #PythonProgramming #ProjectManagement #LPsolvers #Primavera #MSProject #TransportationProblem #CPLEX #IndustrialOptimization